Physics Questions and Answers
If you want to learn more about the nature and properties of matter and energy or you're simply preparing for a Physics exam, these Physics past questions and answers are ideal for you.

If you want to learn more about the nature and properties of matter and energy or you're simply preparing for a Physics exam, these Physics past questions and answers are ideal for you.
A rainbow is formed when sunlight is incident on water droplets suspended in the air due to
interference
refraction
dispersion
diffraction
Correct answer is C
No explanation has been provided for this answer.
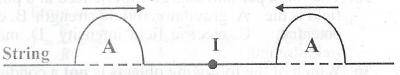
0
\(\frac{A}{2}\)
\(\frac{A}{4}\)
\(2A\)
Correct answer is D
This is a type of constructive interference. When two waves of equal amplitude are interfering constructively, the resulting amplitude is twice as large as the amplitude of an individual wave.
= A + A = 2A
A vapour whose molecules are in dynamic equilibrium with those of its own liquid is said to be
unsaturated
gaseous
saturated
diffused
Correct answer is C
A saturated vapour is one which is in a dynamic equilibrium with its own liquid
The maximum density of water occurs at a temperature of
0°C
4°C
37°C
273°C
Correct answer is B
This is as a result of the Hydrogen bonding in water. Due to the high Kinetic Energy of water, the hydrogen bonds can't hold for too long but from 4°C, there's an increase in the hydrogen bonds hence strenghtening it. From the point of production of more hydrogen bonds, the bonding is no longer easily broken. Generally, these and a few factors based on these cause the density of water to be maximum at 4°C.
Thermal energy added or removed from a substance that changes the state of the substance is called
latent heat
heat of reaction
calorimetry
specific heat
Correct answer is A
Latent heat is thermal energy released or absorbed, by a body or a thermodynamic system, during a constant-temperature process.