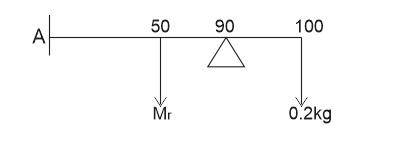
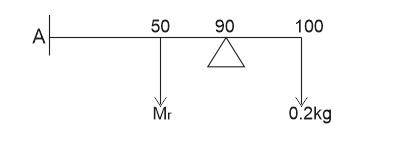
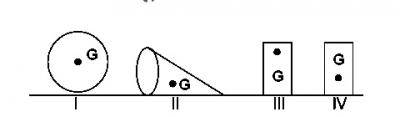
206.
The equilibrium position of objects in any field corresponds to situation of
A.
equipotential energy
B.
maximum potential energy
C.
minimum potential energy
D.
minimum kinetic energy
Correct answer is C
Potential energy = mgh = (mg)h = force × distance
⇒ 0 × d = 0
209.
The volume of a stone having an irregular shape can be determined using?
A.
meter rule
B.
measuring cylinder
C.
vernier calliper
D.
micrometer screw gauge
Correct answer is B
The volume of object is the same as the volume of liquid displaced in a container such as measuring cylinder.
JAMB Subjects
Aptitude Tests