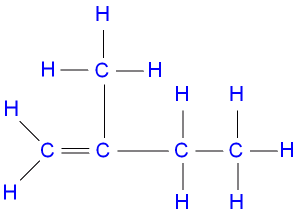
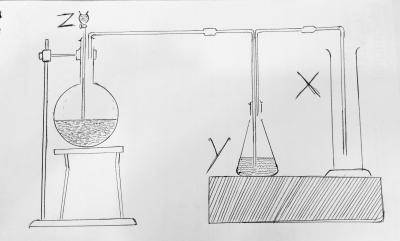
Chemistry Questions and Answers
Learn more about the properties, composition, and structure of substances (elements and compounds) with these Chemistry questions and answers. This Test can be used by students preparing for Chemistry in JAMB, WAEC, NECO or Post UTME.