\(\frac{2}{5}\)
\(\frac{5}{2}\)
\(\frac{2}{7}\)
\(\frac{7}{2}\)
Correct answer is A
Gradient(slope) m = \(\frac{ y_2 - y_1}{ x_2 - x_1}\)
the points are \((\frac{1}{2}, \frac{- 1}{3}) and ( 3 , \frac{2}{3})\)
m = \(\frac{\frac{2}{3} - (\frac{-1}{3})}{3 - \frac{1}{2}}\)
= \(\frac{\frac{2}{3} + \frac{1}{3}}{3 - \frac{1}{2}}\)
= \(1 \div\frac{5}{2}\) = \(1\times\frac{2}{5}\)
Therefore, m = \(\frac{2}{5}\)
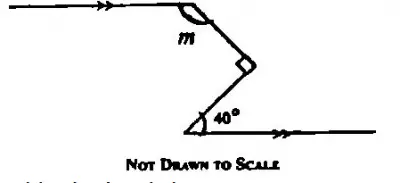
Find the value of m in the diagram above.
\(40^0\)
\(50^0\)
\(130^0\)
\(140^0\)
Correct answer is C
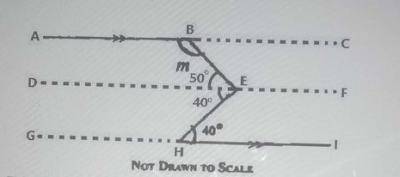
∠EHI = ∠DEH = 40° (alternate angles are equal)
∠BEH = 90° (given)
∠BED = 90° - 40° = 50°
∠BEF = 180° - 50° = 130° (sum of angles on a straight line is 180o)
∠BEF = ∠ABE = 130° (alternate angles are equal)
∴ m = 130°
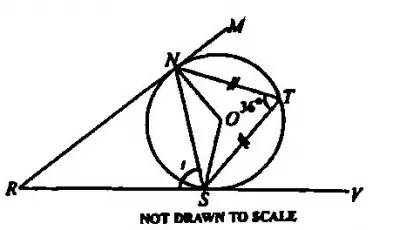
\(72^0\)
\(54^0\)
\(36^0\)
\(108^0\)
Correct answer is C
t = ∠NTS (the angle between a tangent and a chord is equal to the angle in the alternate segment).
Therefore, t = 36°
The length of the diagonal of a square is 12 cm. Calculate the area of the square.
\(36 cm^2\)
\(48 cm^2\)
\(72 cm^2\)
\(18 cm^2\)
Correct answer is C
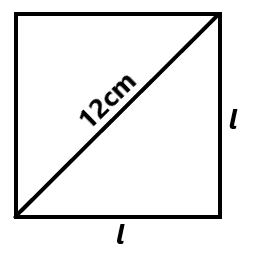
Let each side be l, then area = \(l^2\)
Using Pythagoras theorem
\(l^2 + l^2 = 12^2\)
\(2l^2 = 144\)
divide both sides by 2
\(l^2 = 72\)
Therefore, the Area of the square is \(72 cm^2\)
Find the quadratic equation whose roots are \(\frac{2}{3} and \frac{- 3}{4}\)
\(12y^2 - y - 6 = 0\)
\(12y^2 - y + 6 = 0\)
\(12y^2 + y - 6 = 0\)
\(y^2 + y - 6 = 0\)
Correct answer is C
Let p = \(\frac{2}{3}\) and q = \(\frac{- 3}{4}\)
using (y - p)(y - q) = 0
= ( y - \(\frac{2}{3})\)( y - (\(\frac{- 3}{4})) = 0\)
= (\( y - \frac{2}{3})( y + \frac{3}{4})\) = 0
\( y^2 + \frac{3}{4}y - \frac{2}{3}y - \frac{6}{12} = 0 \)
\( y^2 + \frac{1}{12}y - \frac{1}{2}\) = 0
= multiply through by the l. c. m of 3 and 4 = 12
∴ the quadratic equation is \(12y^2 + y - 6 = 0\)
WAEC Subjects
Aptitude Tests